What is Cloud Hosting?
Cloud hosting is the next iteration of hosting. Cloud Hosting can be definied as a type of internet hosting where the client leases virtualized, dynamically scalable infrastructure on an as-needed basis. Cloud hosting had been creating quite a buzz around these days. Cloud hosting is a web hosting service delivered from a group of connected servers. In general, a hosting service can be considered cloud hosting when it is delivered from a fully redundant, multi-server system, in which the resources are dynamically scalable and often virtualized.
Cloud hosting basically means instead of your usual one server based hosting, it uses many servers to keep data running across them, meaning if one goes down then your site doesn’t, its faster and more efficient. You might be hearing the phrase ’cloud hosting’ for the first time but the technology is not something new at this time of writing. In fact, you’re already part of the cloud hosting/computing users (without being noticed) as Google naturally is a big promoter of this idea. Google searches (as well as other Google operations) are operating under a massive computer infrastructure (cloud) that people tap into from their local computers.
Cloud hosting is the practice of running Web applications in a "cloud"; a collection of external, virtual servers that are interconnected, either on a corporate network or via the public Internet. The idea behind cloud hosting is to give customers a resource that is highly scalable, reliable and available, with little or no regard to the system’s underlying technology or physical location.
Generally, website hosted on a cloud hosting operates on a clustered servers where online operations are not limited to a single server. By handling security, load balance and hardware resources virtually, the website has access to the processing power of a number of servers that are distributed in real time.
Cloud Hosting Benefits
Cloud hosting benefits the users from various angles. It’s scalability and cost efficient is the commonly known advantages. As the technology is highly scalable, website expansion can be done without the limitation in server resources. Think about the hassle of migrating your website from a shared server to a dedicated server; think about server crash when your website experienced a sudden surge - with the scalability of cloud hosting, all these problem can be avoided easily.
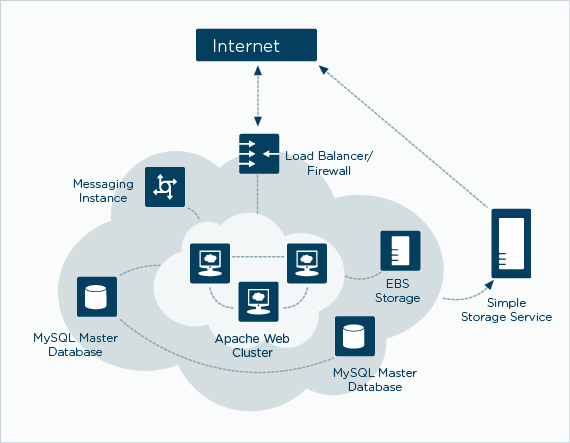
Cloud Hosting is using the utilities billing model. In basic terms, a client only pays for the resources he uses, just like your electricity bill or water rates. You pay for CPU usage, memory and bandwidth and it scales as and when you need it. This stands true only in the case of Cloud Computing. Otherwise, the term cloud is often interpreted by the service providers the way they want and most of them are trying to sell plain VPS in the name of Cloud. Imagine being able to provision a server in minutes or upgrade a server automatically. To bring servers up and down as needed. This is the idea behind Cloud Servers. Totally customizable, each Cloud Server gives you full root access to your Linux distribution of your choice. Your price depends on how large a server you buy.
Cloud hosting companies charge their users based on the quantity of computing power used. It’s like your electricity and water supply bills - it’s pay-per-use. Gone are the days where you need to reserve high server powers in order to avoid website crash, server resources are now used on demand.
Some people would explain cloud computing through virtualization. I disagree with them because I consider a computer cloud as a number of nodes (computers or servers) connected into a network. They enable consolidation, sharing and distribution of compute resources, load-balancing, etc. However what makes a network of computers to works together as a cloud is the automation platform which runs on top.
Cloud Hosting Providers
Mosso, RakeSpace, Amazon, and GoGrid are some of the biggest names in cloud computing/storage hosting world.