What is Rotavirus - Causes and Symptoms
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), “before the vaccine, more than 200,000 U.S. children were taken to emergency rooms and more than 55,000 were hospitalized each year with rotavirus, which causes vomiting and diarrhea, mostly from January through May. Worldwide, the virus kills 1,600 young children each day.”
In 1998, a rotavirus vaccine was approved for use in children. However, the vaccine is no longer recommended for use in the United States because of data that indicated a strong association between the vaccine and bowel obstruction in some infants during the first 1-2 weeks after vaccination.
 What is Rotavirus?
What is Rotavirus?
Rotavirus is caused by a virus. Rotavirus infection is a viral infection of the digestive tract. It is the most common cause of severe diarrhea in infants and young children in the United States.
What can rotavirus do to my child?
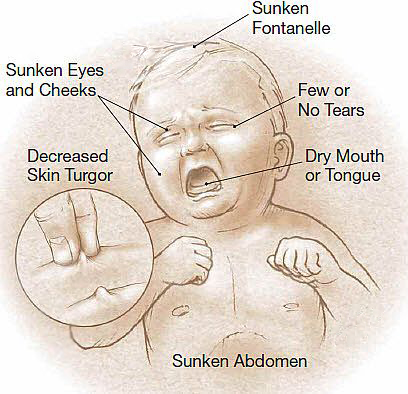
Rotavirus can cause severe diarrhea, vomiting, fever, stomach pain and dehydration.Among younger children, Rotavirus can cause severe illness or even death due to dehydration
Is my child at risk?
Yes! All children are at risk.
What can I do to protect my child against Rotavirus?
Please ask your doctor how to help protect your child and the latest Immunization techniques such as Vaccination to protect from Rotavirus.
How does it spread?
- Rotavirus is found in the stool of infected. Rotavirus is easily spread by hand-to-mouth contact with stool from an infected person.
- Most children with rotavirus diarrhea recover on their own. Some children become very ill with severe vomiting, diarrhea, and life-threatening loss of fluids that requires hospitalization.